Key Measures to Control Pharmaceutical Contamination
The control and prevention of contamination are paramount in the pharmaceutical industry to ensure the safety and quality of products. The presence of contaminants, such as microbes, dust, and particles in pharmaceutical products, may not only affect their quality and safety but also impact business credibility and sustainability. Pharmaceutical contamination, particularly in sterile products, can be costly to companies due to non-compliance.
Therefore, implementing definitive contamination prevention and due diligence strategies like proper cleanroom suits is essential to maintain a safe and hygienic sterile environment.
Let’s explore the key strategies to help control and prevent contamination in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Identify the Source of Pharmaceutical Contamination
The primary step in controlling contamination in the pharmaceutical industry is identifying the source of contaminants. It is not enough to just maintain optimal bio-burden levels through cleaning and disinfection; understanding the occurrence of contaminants and addressing them is critical. The potential sources of contamination include:
- Personnel
- Manufacturing Facility
- Materials
- Manufacturing Process
Prevent Contamination through Personnel
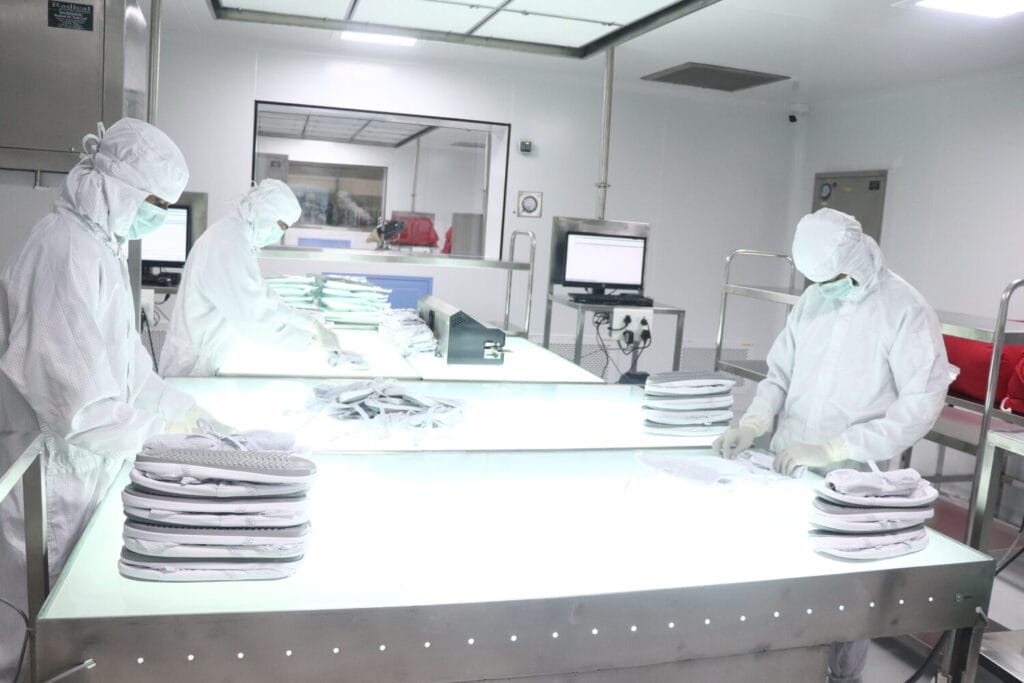
Workers who oversee or control pharmaceutical manufacturing, packing, and transportation are major sources of contamination. This primarily occurs due to a lack of training or inadequate regulatory and hygiene standards. Here are some ways to control contamination through personnel:
- Train all workers directly involved with product manufacturing and handling hygiene standards.
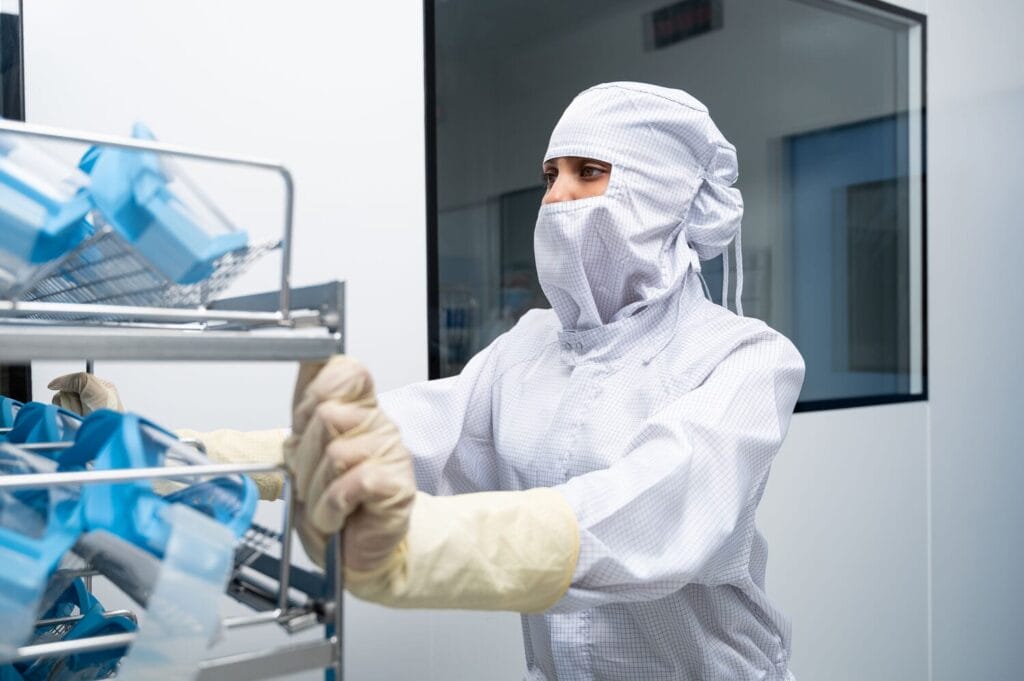
- Standardize the mandatory use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), including hand gloves, face masks, overshoes, hair caps, any piece of laboratory uniform, and cleanroom suits inside the manufacturing unit.
- Ensure workers maintain high levels of personal hygiene.
- Practice proper and regulatory-compliant workwear cleaning and disinfection measures.
- Avoid direct contact between the worker’s hand and any part of the product.
- Regulate access to production areas to ensure that only trained personnel can enter the manufacturing unit.
Building Requirements for De-contamination
The design and quality of the building can also be a potential source of pharmaceutical contamination. Building hygiene can be maintained by:
- Ensuring interior surfaces like ceilings, walls, and floors are smooth and free from cracks to facilitate effective cleaning
- Sealing viewing panels and windows to prevent collection of microbes, dust, and particles
- Installing stainless steel sinks inside the manufacturing unit
- Designing light points, ventilation, and pipework to enable efficient cleaning
Manufacturing Facility Design
To prevent contamination inside the manufacturing facility, high hygiene standards, regulatory compliances, and optimal design must be implemented. Here are some key steps to control facility contamination:
- Maintain aseptic process rooms at high differential air pressure.
- Avoid uncomfortable levels of ambient humidity or temperature.
- Based on product risk assessment/facility, use a Restricted Access Barrier System, Isolators Systems, Ventilated Cabinets, etc., to help contain microorganisms.
- Maintain a laminar flow of air with optimal velocity over critical areas.
- Use ultraviolet door barriers and airlocks to separate areas.
- Implement impermeable barriers such as vacuum or pumped transfer of materials, closed systems, etc., to prevent cross-contamination.
- Adequately set air change and air filtration rates to maintain statutory cleanroom standards.
- Thoroughly maintain and monitor surfaces and rooms to identify viable and non-viable particles; recertify the facility every six months.
- Ensure the HVAC system is designed and located to prevent contaminants from spreading inside the room.
Hygiene and Disinfection
Proper cleaning, hygiene, and sanitization measures should be practised throughout the building, manufacturing facility, and storage units:
- Clean and disinfect all areas regularly
- Use only fully trained personnel to handle cleaning agents and minimize health risks with the right cleanroom suits.
- Consider the application, contact time, chemistry, mechanical action, and temperature of the cleaning agent while designing the cleaning process.
- Ensure cleaning materials don’t come in direct contact with pharmaceutical products.
- Regulate cleaning practices throughout the building and manufacturing unit to control and eliminate microbial contamination effectively.
Prevent Contamination through Utilities
Water is one of the most significant sources of bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants, affecting pharmaceutical product quality and patient safety. Control water-borne contamination by:
- Using microbiologically controlled, pharmaceutical-grade water, appropriates for the intended use in the manufacturing process.
- Ensuring steam, humidification, and supply for autoclaves are free of additives and clean
I
n conclusion, failure to maintain optimal pharmaceutical contamination control measures can have detrimental repercussions on the quality and safety of products. Lindstrom supports pharmaceutical companies by providing professional and reliable workwear rental services in India. We maintain the highest standards of hygiene and comply with regulatory standards to design, maintain, transport, and replace workwear. Our cleanroom services provide clean and fully disinfected uniforms, helping control contamination through personnel.



